Practical AI: Using NLP word vectors in a novel way to solve the problem of localization
The most practical use of word embeddings (word2vec, glove, etc) you will ever see.
Ramsri GouthamFollowAug 31 · 5 min read

King — Man + Woman = Queen
You might have seen the traditional word2vec or Glove word embeddings examples that show King -Man+Woman = Queen. Here Queen will be returned from the word embedding algorithm given the words King, Man, and Woman. Today we will see how we can use this structure to solve a real-world problem.
1. The problem definition:

An edtech company in the USA wants to expand into India after being successful in its home market. It has a large set of questions in their question bank that it wants to use when it enters the Indian market.
But there is one big problem. A sample third class (grade) math question in their question bank looks like this —
Frank lives in San Francisco and Elizabeth lives in Los Angeles. If the flight time is 2 hrs when will Elizabeth reach Frank if she starts at 8am in the morning?
A 3rd-grade kid living in India would not connect with this question as it has references to names and locations lesser know to him/her – Frank, San Franciso, Los Angeles, etc.
So it would be ideal if we change the question to suit the Indian context and rephrase it—
Sanjay Verma lives in Bangalore and Rekha lives in Mumbai. If the flight time is 2 hrs when will Rekha reach Sanjay Verma if she starts at 8am in the morning?
This concept is called localization. It is the general concept of adopting a product or idea to a different country or region respecting local norms, customs, and any other preferences. The goal is to resonate with the target audience for whom the content is localized.

2. The word embeddings approach:
Now let’s look at how we can localize our original USA math question to the Indian context.
Frank lives in San Francisco and Elizabeth lives in Los Angeles. If the flight time is 2 hrs when will Elizabeth reach Frank if she starts at 8am in the morning?
Step 2.1: Our goal is to extract all the keywords that need to be localized. We will use the Spacy Named Entity Recognition to achieve this.

Step 2.2: Filter named entities that are irrelevant. For example entities like numbers (cardinal) and time doesn’t need localization in our case.
Filtered entities: Frank, San Franciso, Elizabeth, Los Angeles
Step 2.3: Now comes the most interesting part. We will use the King-Man + Woman = Queen framework to convert each of the entities. The code is present in the next sections but here we only show the concept.
Frank-USA+India = Sanjay Verma
San Franciso-USA+India = Bangalore
Elizabeth-USA+India = Rekha
Los Angeles-USA+India = Mumbai
Step 2.4: We go back and change the entities with their replacements to get –
Sanjay Verma lives in Bangalore and Rekha lives in Mumbai. If the flight time is 2 hrs when will Rekha reach Sanjay Verma if she starts at 8am in the morning?
3. Enough talk, show me the code 🙂
Google ColaboratoryEdit descriptioncolab.research.google.com
Check out the complete and clean Google Colab notebook, that shows two different localization examples. The first example is automated and the second one has simple UI to choose the best replacement manually.
The important parts are shown here in code again (besides Colab)—
Step 3.1 Extract entities that need to be localized
import spacy
import pandas as pd
from spacy import displacy
from spacy.tokens import Span
nlp = spacy.load("en")original_input = "Frank lives in San Francisco and Elizabeth lives in Los Angeles. If the flight time is 2 hrs when will Elizabeth reach Frank if she starts at 8am in the morning?"
processed_input_text=nlp(original_input)
keyword_set = set()
entity_mapping = []
for token in processed_input_text.ents:
if token.text not in keyword_set:
keyword_set.add(token.text )
entity_mapping.append((token.text,token.label_))
print (entity_mapping)
displacy.render(processed_input_text, style='ent', jupyter=True)# Now all entities cannot be localized. Example no need to localize numbers. So keep only relevant entities that need to be localized.
keep_entities_list = ['PERSON','GPE','FAC','ORG','PRODUCT','NORP','MONEY','LOC','WORK_OF_ART','LAW','LANGUAGE','QUANTITY']
finalized_entity_mapping = {}
for ent in entity_mapping:
if ent[1] in keep_entities_list:
finalized_entity_mapping[ent[0]] = []print (finalized_entity_mapping)
The output from the above step is —
Unfiltered entities:
[('Frank', 'PERSON'), ('San Francisco', 'GPE'), ('Elizabeth', 'PERSON'), ('Los Angeles', 'GPE'), ('2', 'CARDINAL'), ('8am in the morning', 'TIME')]Entities after filtering:
{'Frank': [], 'San Francisco': [], 'Elizabeth': [], 'Los Angeles': []}
Step 3.2 Initialize the Google news word vectors from Gensim and perform localization
import gensim.downloader as api
model = api.load("word2vec-google-news-300")
word_vectors = model.wvOrigin_country='USA'
Target_country='India'final_mapping ={}for word in finalized_entity_mapping:
word = word.strip()
word = word.replace(" ","_")
try:
similar_words_list= model.most_similar(positive=[Target_country,word],negative=[Origin_country],topn=10)
# Remove the scores for the retrieved choices
similar_words_list = [choices[0].replace("_"," ") for choices in similar_words_list ]
final_mapping[word.replace("_"," ")] = similar_words_list
except:
similar_words_list = []
print (" Fetching similar words failed for ",word)
print (word," -- Replacement suggestions -- ",similar_words_list)
The output from the above step is —
Frank -- Replacement suggestions -- ['Sanjay Verma', 'Sabyasachi Sen', 'JK Jain', 'Sunil Chauhan', 'Don', 'Sudip', 'Ajay Shankar', 'Robert', 'V. Srinivasan', 'Kanwar Sain']San_Francisco -- Replacement suggestions -- ['Bangalore', 'Kolkata', 'Mumbai', 'Chennai', 'Delhi', 'Hyderabad', 'Calcutta', 'San Franciso', 'Bombay', 'Bengaluru']Elizabeth -- Replacement suggestions -- ['Rekha', 'Nandita', 'Meera', 'Margaret', 'Katharine', 'Bhagirath', 'Monica', 'Lakshmi', 'Manisha', 'Anita']Los_Angeles -- Replacement suggestions -- ['Mumbai', 'Los Angles', 'Kolkata', 'Chennai', 'Bangalore', 'LA', 'Delhi', 'Hyderabad', 'Ahmedabad', 'Calcutta']
You can see each word along with its top replacement choices.
Step 3.3 Print the output with its replacement
def localize(sentence,mapping):
for k in mapping:
sentence = sentence.replace(k,mapping[k][0])
return sentenceprint('Original Sentence:')
print(original_input)localized_string = localize(original_input,final_mapping)print('\nLocalized Sentence:')
print(localized_string)
The output is —
Original Sentence:
Frank lives in San Francisco and Elizabeth lives in Los Angeles. If the flight time is 2 hrs when will Elizabeth reach Frank if she starts at 8am in the morning?Localized Sentence:
Sanjay Verma lives in Bangalore and Rekha lives in Mumbai. If the flight time is 2 hrs when will Rekha reach Sanjay Verma if she starts at 8am in the morning?
Great! We are finally near the finish line.
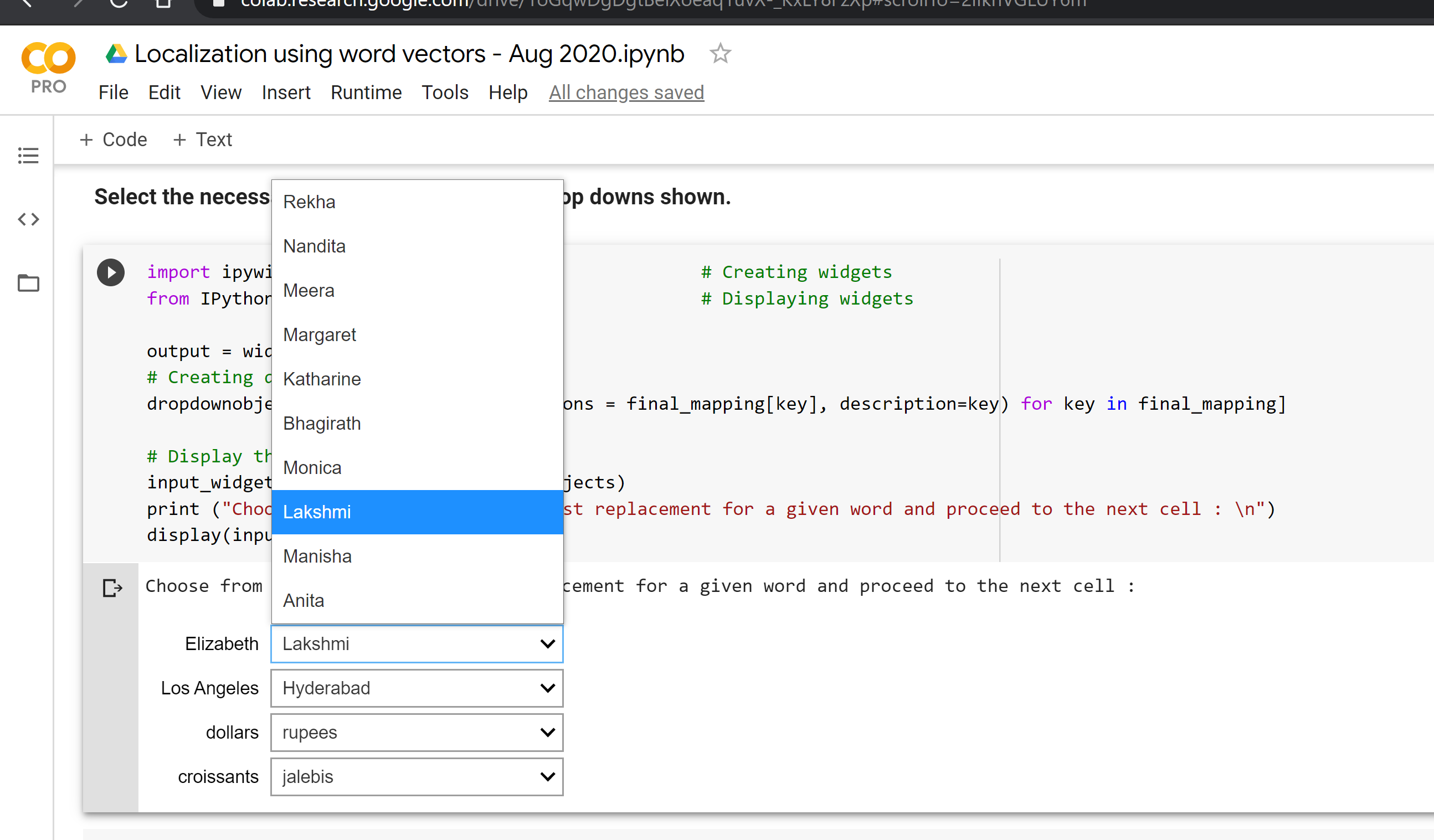
But what if the first choice shown is not the correct replacement for a given word?
To fix that problem, we built a small UI to select the correct choice with a dropdown. It is shown in the Google Colab notebook under example 2.
This project is carried out by the awesome intern Niharika Reddy, under my mentorship as a part of my open-source initiative Questgen.ai